
Silver features printed on conformal bladder.

Silver features printed on radome
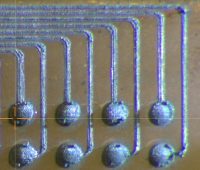
Close-up view of interconnect pads
In choosing an aerosol technology over inkjet, one needs to consider the material sets (inks and substrates) as well as performance features of one technology over another.
| Ink Types | Function | Application |
|---|---|---|
| Nanoparticle Silver | Conductor | Electrical interconnects, metallic films, metal bumps |
| Nanoparticle Gold | Conductor | Electrical interconnetions, biodevices, metal bumps |
| Particle-Free Silver | Conductor | Metallization of polymers, multi-layer circuit fabrication |
| Polymeric Solution | Insulator | Multi-layer applications |
| Particle-free Gold | Conductor | Metallization of heat-sensitive materials (processing temps < 125°C) |
Inks
Inks well suited for interconnect printing include silver, gold, nanoparticle conductive inks, polymer insulating inks, and particle-free conductive inks. The ability to print or layer conducting and non-conducting features provides tremendous opportunity for the design engineer to create compact, lightweight devices.
Materials
The material sets that inkjet and aerosol printing can serve are similar, though aerosol printing can generally tolerate higher viscosity inks (1 -50 mPa⋅s). Further, aerosol printing is better suited than inkjet to print complex circuits or patterns on non-planar substrates.
Substrates
Aerosol and inkjet direct-write technologies are more “flexible” with regards to stiffness of substrates than either web-based printing solutions which require flexible substrates or photolithography solutions which perform better with stiff substrates. Aerosol printing has been demonstrated on non-planar bladders which are not only flexible, but also defiantly non-planar.
Typical substrates used in aerosol printing may include: Kapton®, polyester, borosilicate glass, fiber-reinforced nylon, silicon, polyimides, ITO coatings (Indium Tin Oxide), alumina, and FR4.
| Substrate | Function | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Kapton® | Flex Substrate | Common & flexible |
| Silicon | Semiconductor | Microelectronic apps |
| Glass | Display | Flat panels |
| FR4 | Rigid Substrate | Common electronics |
